Kubernetes came into the picture after the Software development teams started switching from monolithic and microservices architecture to containerization because of scalability and deployment issues. Containerization does solve the issue of scalability, downtime and dependency management quite efficiently however there are still some issues that remain unsolved.
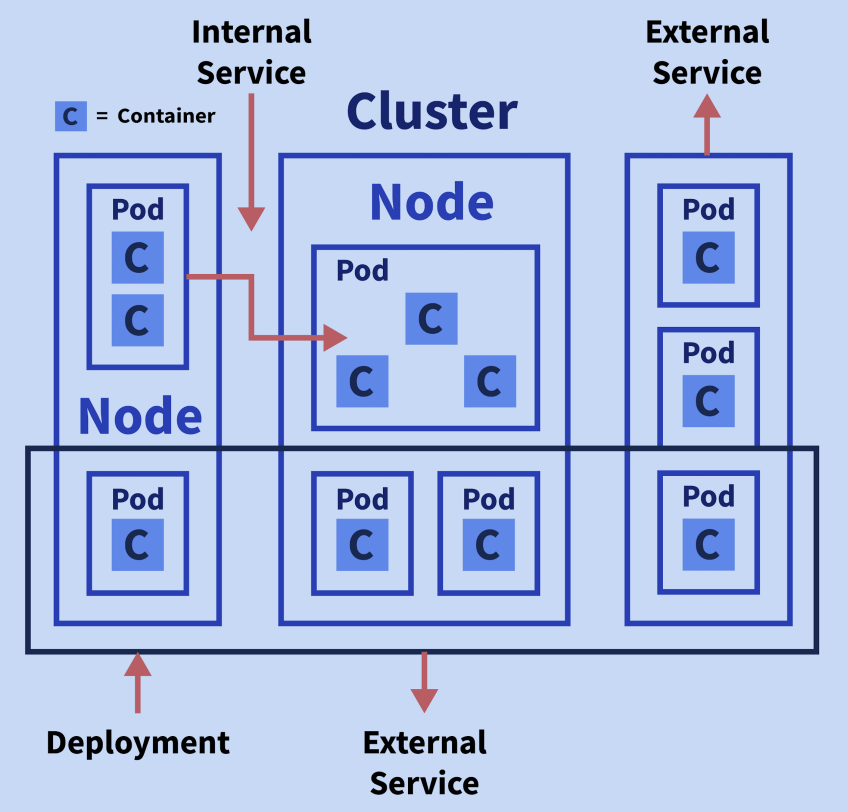
Kubernetes Terminology
Terms that you should be familiar with before starting off with Kubernetes are enlisted
below:
| K8S Terms | Explanation |
| Cluster | It can be thought of as a group of physical or virtual servers where Kubernetes is installed. |
| Nodes | There are two types of Nodes, 1. Master node is a physical or virtual server that is used to control the Kubernetes cluster. 2. Worker node is the physical or virtual server where workload runs in given container technology. |
| Pods | The group of containers that shares the same network namespaces. |
| Labels | These are the key-value pairs defined by the user and associated with Pods. |
| Master | It controls plane components to provide access points for admins to manage the cluster workloads. |
| Service | It can be viewed as an abstraction that serves as a proxy for a group of Pods performing a "service". |
Kubernetes Commands
1. Nodes:
A Node is a worker machine in Kubernetes and may be either a virtual or a physical machine, depending on the cluster. Each Node is managed by the control plane. A Node can have multiple pods, and the Kubernetes control plane automatically handles scheduling the pods across the Nodes in the cluster.
| Commands | Description |
| kubectl get node | To list down all worker nodes. |
| kubectl delete node | Delete the given node in cluster. |
| kubectl top node | Show metrics for a given node. |
| kubectl describe nodes | grep ALLOCATED -A 5 | Describe all the nodes in verbose. |
| kubectl get pods -o wide | grep | List all pods in the current namespace, with more details. |
| kubectl get no -o wide | List all the nodes with mode details. |
| kubectl describe node | Describe the given node in verbose. |
| kubectl annotate node | Add an annotation for the given node. |
| kubectl uncordon node | Mark my-node as schedulable. |
| kubectl label node | Add a label to given node |
2. Pods
Pods are the smallest deployable units of computing that you can create and manage in Kubernetes.
| Commands | Description |
| kubectl get pod | To list the available pods in the default namespace |
| kubectl describe pod | To list the detailed description of pod. |
| kubectl delete pod | To delete a pod with the name. |
| kubectl create pod | To create a pod with the name |
| Kubectl get pod -n <name_space> | To list all the pods in a namespace. |
| Kubectl create pod <pod_name> -n <name_space> | To create a pod with the name in a namespace. |
3. Namespaces
In Kubernetes, namespaces provide a mechanism for isolating groups of resources within a single cluster. Names of resources need to be unique within a namespace, but not across namespaces.
| Commands | Description |
| kubectl create namespace <namespace_name> | To create a namespace by the given name. |
| kubectl get namespace | To list the current namespace in a cluster. |
| kubectl describe namespace <namespace_name> | To display the detailed state of one or more namespaces. |
| kubectl delete namespace <namespace_name> | To delete a namespace. |
| kubectl edit namespace <namespace_name> | To edit and update the definition of a namespace. |
4. Services
In Kubernetes, a Service is an abstraction which defines a logical set of Pods and a policy by which to access them (sometimes this pattern is called a micro-service).
| Commands | Description |
| kubectl get services | To list one or more services. |
| kubectl describe services | To list the detailed display of services. |
| kubectl delete services -o wide | To delete all the services. |
| kubectl delete service < service_name> | To delete a particular service |
5. Deployments
A Deployment provides declarative updates for Pods and ReplicaSets.The typical use case of deployments are to create a deployment to rollout a ReplicaSet, declare the new state of the pods and rolling back to an earlier deployment revision.
| Commands | Description |
| kubectl create deployment | To create a new deployment. |
| kubectl get deployment | To list one or more deployments. |
| kubectl describe deployment | To list a detailed state of one or more deployments. |
| kubectl delete deployment | To delete a deployment. |
6. DaemonSets
A DaemonSet ensures that all (or some) Nodes run a copy of a Pod. As nodes are added to the cluster, Pods are added to them. As nodes are removed from the cluster, those Pods are garbage collected. Deleting a DaemonSet will clean up the Pods it created.
| Commands | Description |
| kubectl get ds | To list out all the daemon sets. |
| kubectl get ds -all-namespaces | To list out the daemon sets in a namespace. |
| kubectl describe ds [daemonset_name] -n [namespace_name] | To list out the detailed information for a daemon set inside a namespace. |
7. Events
Kubernetes events allow us to paint a performative picture of the clusters
| Commands | Description |
| kubectl get events | To list down the recent events for all the resources in the system. |
| kubectl get events --field-selector involvedObject.kind != Pod | To list down all the events except the pod events. |
| kubectl get events --field-selector type != Normal | To filter out normal events from a list of events. |
8. Logs
Logs are useful when debugging problems and monitoring cluster activity. They help to understand what is happening inside the application.
| Commands | Description |
| kubectl logs <pod_name> | To display the logs for a Pod with the given name. |
| kubectl logs --since=1h <pod_name> | To display the logs of last 1 hour for the pod with the given name. |
| kubectl logs --tail-20 <pod_name> | To display the most recent 20 lines of logs. |
| kubectl logs -c <container_name> <pod_name> | To display the logs for a container in a pod with the given names. |
| kubectl logs <pod_name> pod.log | To save the logs into a file named as pod.log. |
Knowing Kubernetes is a must-have skill whether you are a developer, a tester or a DevOps engineer, I hope this article has helped you out.
